By Hernando Cortina, CFA, Managing Director, ISS ESG.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- European markets have been led by a small number of outperformers known as the “GRANOLAS,” which represent 20% of the market value of the STOXX Europe 600 index. This article examines the sustainability performance of the GRANOLAS compared with the remaining equities in the STOXX Europe 600.
- The article examines six ESG and climate metrics and considers aggregate performance as well as the dispersion in the data. The GRANOLAS financial strength is also reviewed using the Economic Value Added (EVA)-based ISS Financial Rating.
- The GRANOLAS perform very well across overall ESG performance, carbon risk, SDGs, emissions, and temperature scenario alignment, as well as water risk. They also generally perform better than the US companies known as the “Magnificent 7”: GRANOLAS perform similarly to the Magnificent 7 on emissions, temperature, and water risk; meaningfully better on ESG performance and carbon risk; and significantly better on SDGs.
- While the aggregate results provide insight, for investors the most valuable aspect of this analysis might be to understand the dispersion within both groupings at the security level and the specific risks and opportunities individual corporate performance presents.
Europe’s market leaders
Analogous to the sway of the “Magnificent 7” stocks in the US, European markets have been led by a small number of outperformers known as the “GRANOLAS.” As noted in this blog post, these 11 stocks stem from the healthcare, consumer and technology sectors, and are geographically dispersed across the continent. Reflecting their market cap, as of the end of September these equities represented 20% of the market value of the STOXX Europe 600 index.
This article is a companion to the sustainability analysis of the Magnificent 7, examining the sustainability performance of the GRANOLAS compared with the remaining equities in the STOXX Europe 600. The article visualizes identical ESG and climate metrics as in the Magnificent 7 report and considers the aggregate performance as well as the dispersion in the data. Also reviewed is the GRANOLAS’ financial strength using the Economic Value-Added (EVA)-based ISS Financial Rating. The Financial Rating incorporates both profitability and risk, powered by ISS’s proprietary EVA methodology.
Visualizing sustainability metrics
This first metric is the ESG Performance Score. This score evaluates a company’s demonstrated ability to adequately manage material ESG risks, mitigate negative and generate positive social and environmental impacts, and capitalize on sustainable development opportunities. The ESG Performance Score is assessed on a 0-100 scale, with higher values indicating better performance. The score embeds industry-specific E, S, and G indicators weighted by their materiality.
In Figure 1 and all those that follow, the left side shows the indicated metric for the GRANOLAS, while on the right side are the remaining stocks in the STOXX Europe 600 index. Each company is represented by a dot, and a diamond indicates the weighted average of each group. The shading represents the statistical distribution of the companies.
Figure 1: ISS ESG Performance Score
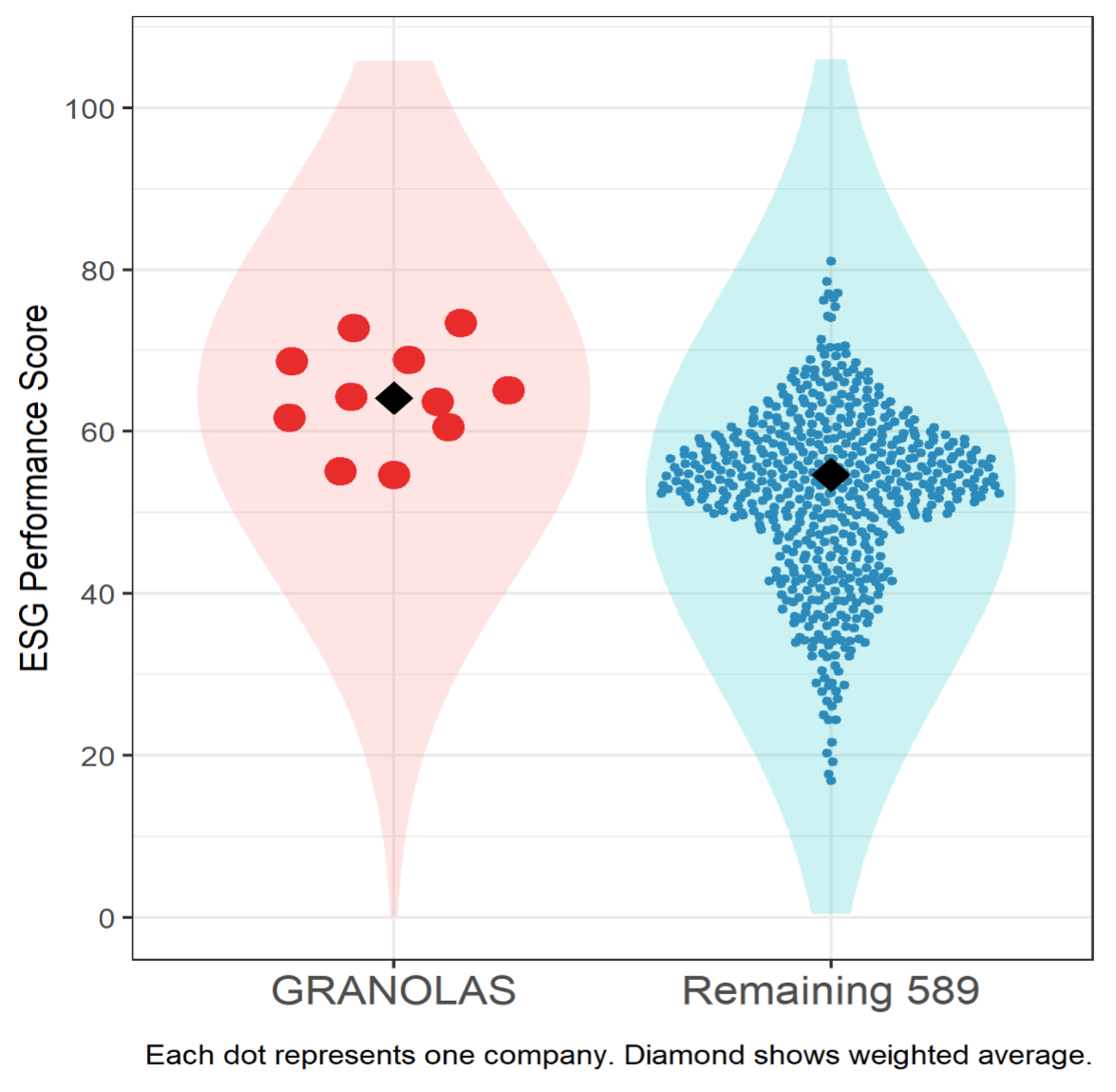
The GRANOLAS score 64.2 while the remaining companies are meaningfully below that, at 54.7. One noteworthy observation is that all 11 stocks have an ESG score above 50, which is the threshold indicating ISS ESG’s Prime status. This designation refers to a company’s demonstrated ability to adequately manage material ESG risks, mitigate negative and generate positive social and environmental impacts, and capitalize on opportunities offered by transformation towards sustainable development. This set of stocks reveals a robust ESG profile, well above the already high-performing European stock market. Even the two lowest stocks sit comfortably above the Prime threshold.
Next, Figure 2 shows the Carbon Risk Rating (CRR), which focuses exclusively on the climate-related performance of companies. The CRR integrates not only CO2 emissions and efficiency, but also the extent to which a company is prepared for the challenges of global warming and can seize opportunities arising from the transition to a low-carbon economy. It is also assessed on a 0-100 scale, with higher values indicating better readiness or lower risk.
Figure 2: ISS ESG Carbon Risk Rating
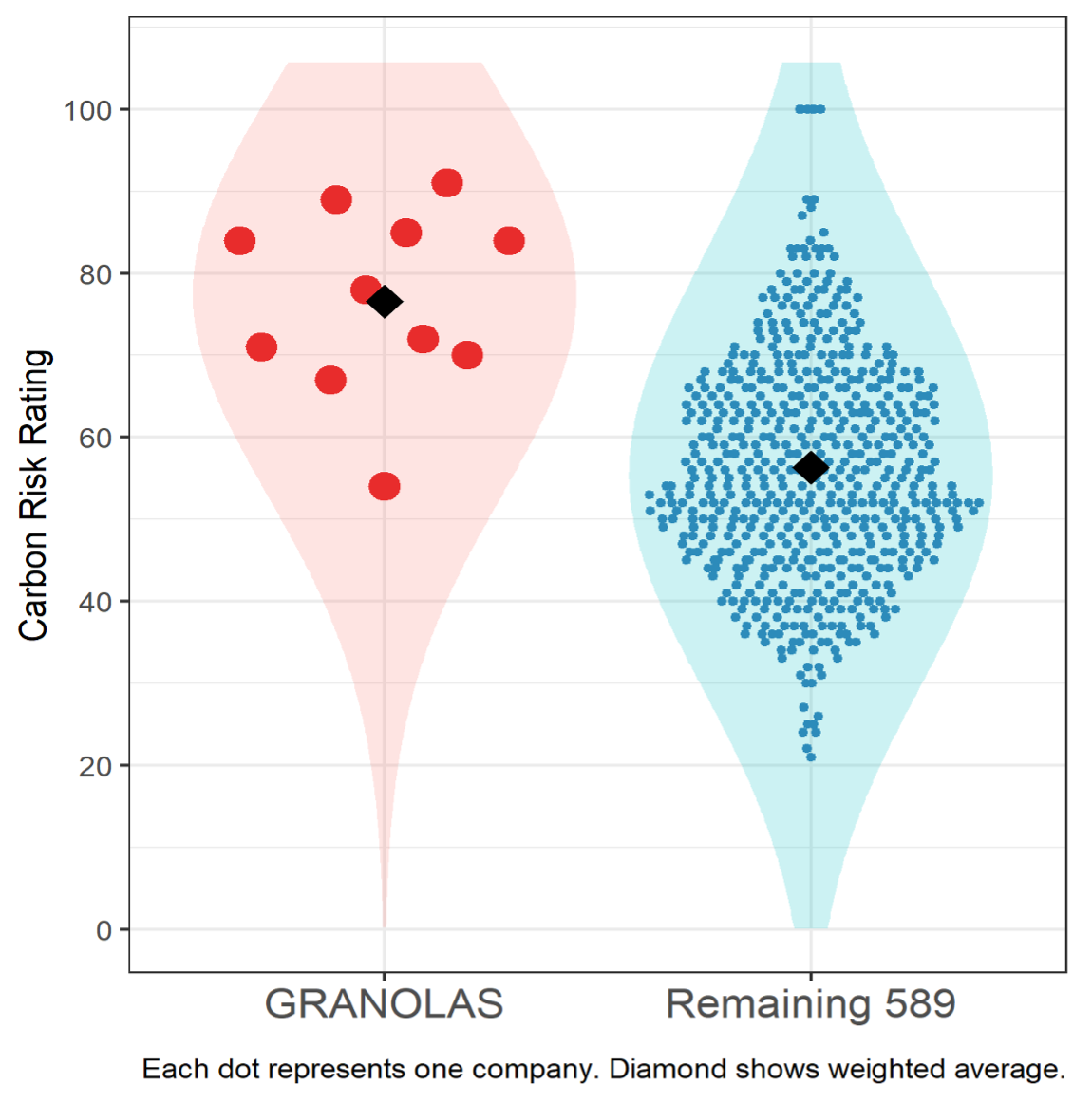
Overall, the GRANOLAS also perform strongly by this measure, scoring 76.5, while the remaining companies are well below that at 56.3. Nonetheless, there is some additional dispersion in the data and some lower-scoring observations. While the GRANOLAS business models are more diverse than the technology-focused Magnificent 7, generally climate-friendly products and services as well as robust climate plans are reflected in outperformance compared with the overall STOXX 600.
The U.N. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a framework for directing investments towards sustainable development priorities. Based on this framework, the ISS SDG Impact Rating holistically scores a company’s positive or negative impact on the 17 SDGs.
Figure 3 shows the overall SDG rating, which is measured on a -10 to +10 scale, with negative values indicating obstruction and positive values indicating alignment. The rating is based on each company’s products and services, operations and controversies. Compared with the ESG rating, the SDG Impact Rating offers a more targeted measure of alignment with global development priorities.
Figure 3: ISS SDG Impact Rating
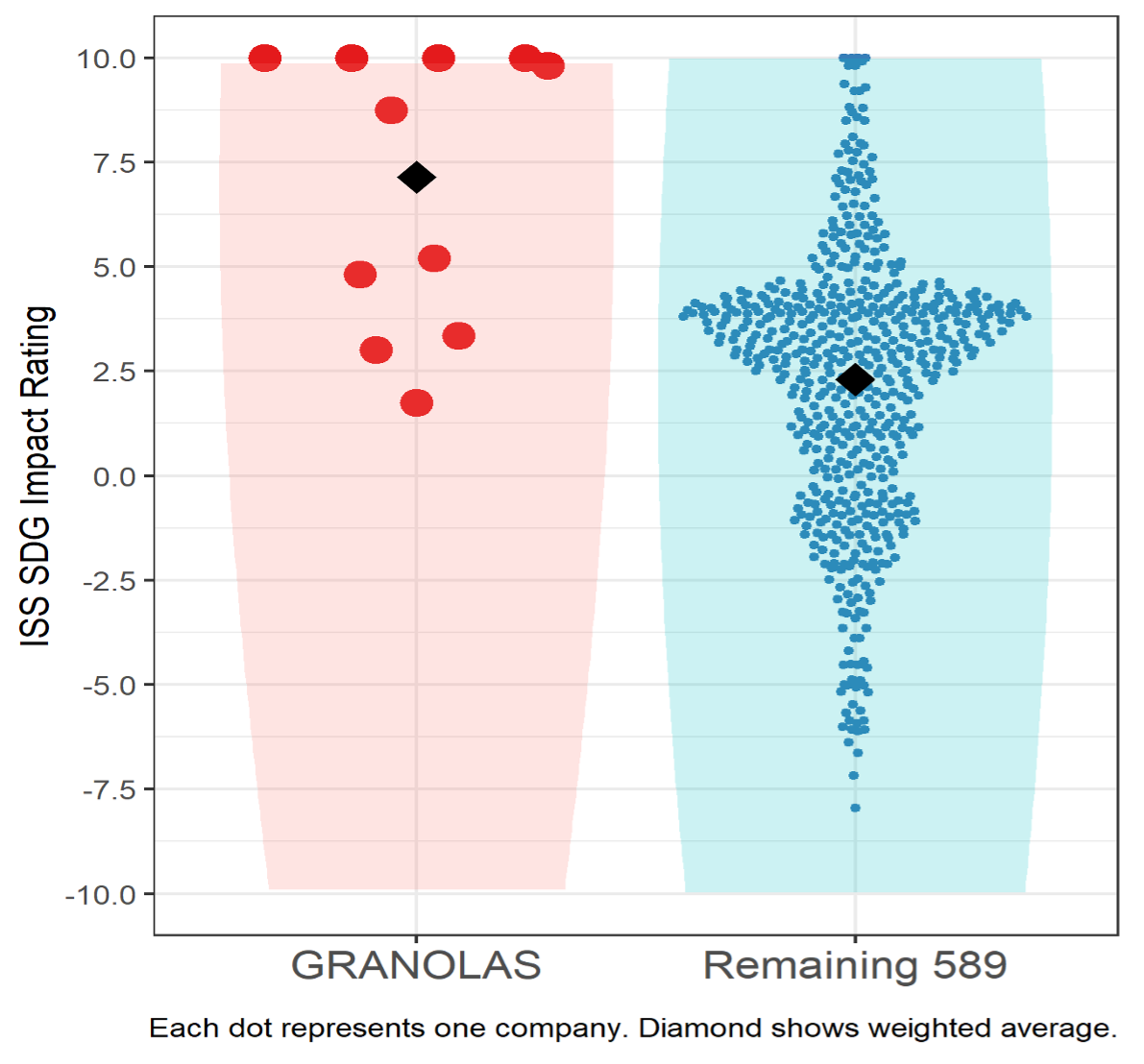
As shown, the GRANOLAS in aggregate and individually perform exceptionally well by this metric, with five of the 11 receiving scores near 10, the highest possible score. Two other companies have scores indicating significant positive contribution to the SDGs, while the remaining 4 show limited but positive contribution to their achievement of the SDGs. None of them show any obstruction to the SDGs. On a weighted average basis, the GRANOLAS perform remarkably above the European market, at 7.1, while the remaining companies are at a still-positive 2.3.
The very strong alignment with the SDGs reinforces the indications from the ESG Performance rating and stands in sharp contrast with the relatively weak SDG alignment of the Magnificent 7, which, on a weighted average basis, was not only below the STOXX USA 500, but only slightly above the neutral value of 0.
While the Carbon Risk Rating provides a forward-looking assessment of preparedness for the low-carbon transition, many investors remain focused on current emissions and emissions intensity, given their importance. Below, Figure 4 shows the Scope 1+2 emissions intensity of these companies. Note that, given the wide dispersion in this data, this is shown on a log scale.
Figure 4: Carbon Emissions Intensity (Scope 1+2 / revenue)
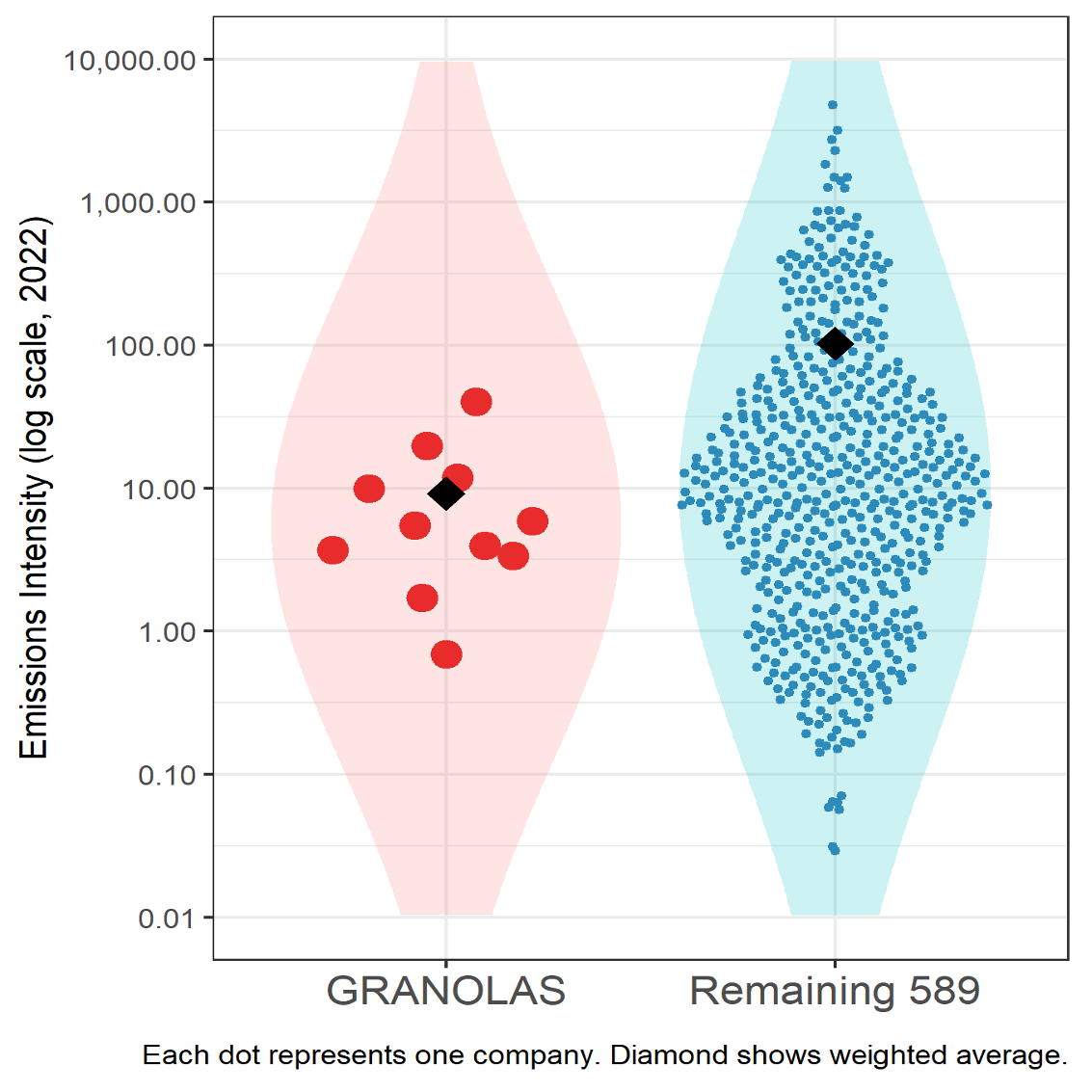
As shown, the GRANOLAS’ emissions intensities are comparatively low, with even the highest intensity company among the eleven performing better than the average of the remaining companies. On a weighted-average basis, the GRANOLAS have a weighted intensity of 9.2 while the remaining companies are at 102.8. It should be noted that, notwithstanding the GRANOLAS’ comparatively impressive performance on emissions intensity, this is a metric that is significantly influenced by these companies’ very large revenues.
A separate forward-looking climate metric is the implied temperature rise (ITR), shown in Figure 5. For every company, given its current and projected emissions, as well as a global carbon budget, this metric provides an assessment of the temperature rise scenario the company aligns with. While a variety of projections and scenarios are available in the ISS climate scenario analysis toolkit, Figure 5 below shows the International Energy Agency’s 2050 Net Zero Scenario alignment, considering company-announced emissions targets. The ITRs range from 1.4° to 6.0°.
Figure 5: Implied Temperature Rise (IEA 2050 Net Zero scenario with company targets)
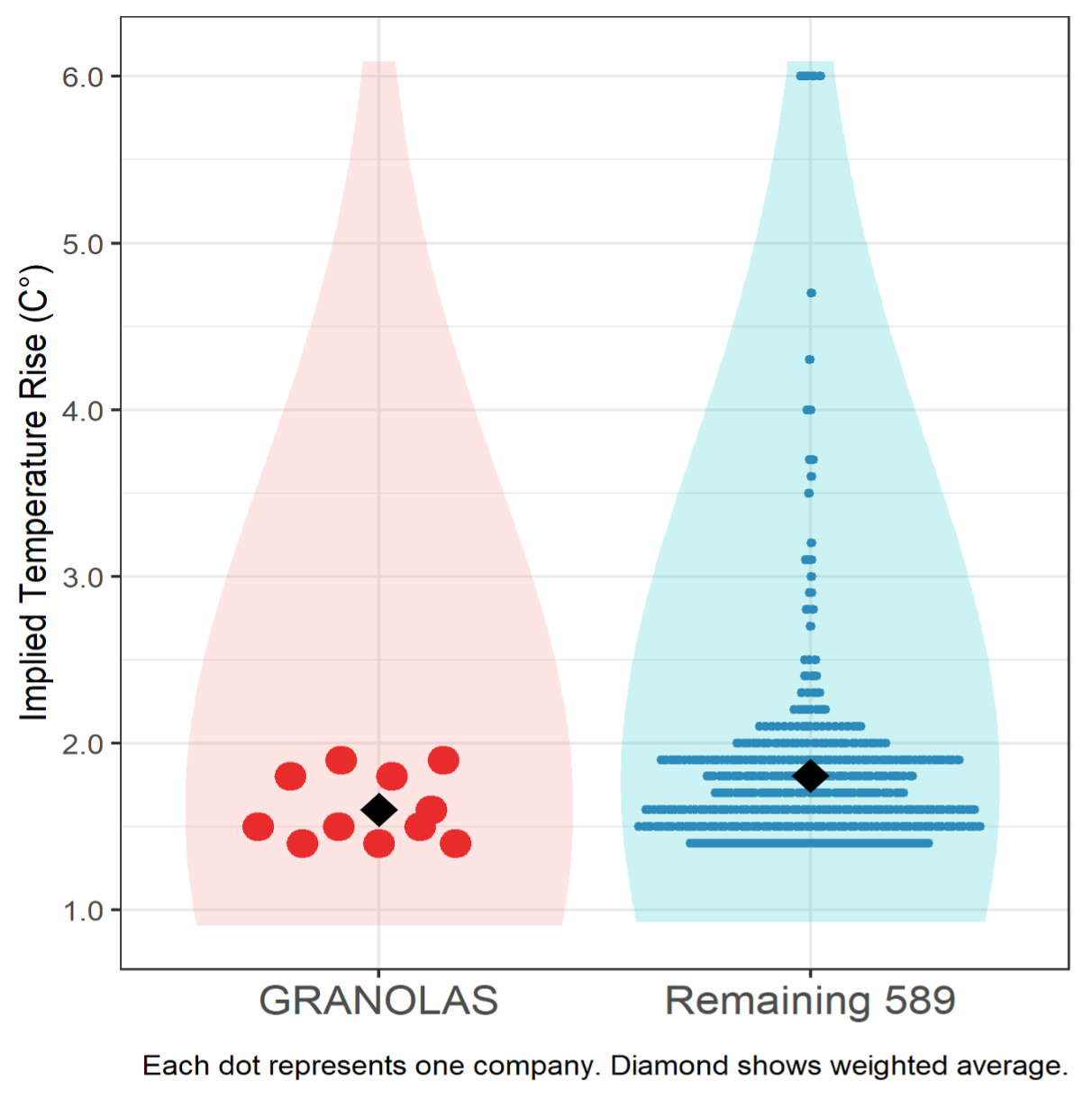
As shown, all the GRANOLAS have ITRs below the 2° C upper limit of the Paris Agreement, while six of them meet the ambitious target of 1.5° C. On a weighted-average basis, the GRANOLAS perform slightly better, 0.2° below the rest of the STOXX 600 index at 1.6°, while the remaining companies are at 1.8°. Furthermore, none are above the Paris upper limit of 2.0°, in contrast to about 14% of the remaining STOXX 600 constituents, which are. While ITRs should not be viewed in isolation of other climate metrics, they provide a straightforward-to-relate-to data point that can aid in climate risk analysis.
The final sustainability metric presented in this analysis, Figure 6, is the Water Risk Rating (WRR). As climate change and increasing demand produce water scarcity in regions of the world, the WRR holistically assesses a company’s exposure to and management of freshwater risks. Exposure consists of a company’s freshwater risks based on its industry, geographic footprint and supply chain. Risk management integrates operational performance and management, as well as relevant controversies. The WRR runs on a scale from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating lower risk.
Figure 6: ISS ESG Water Risk Rating
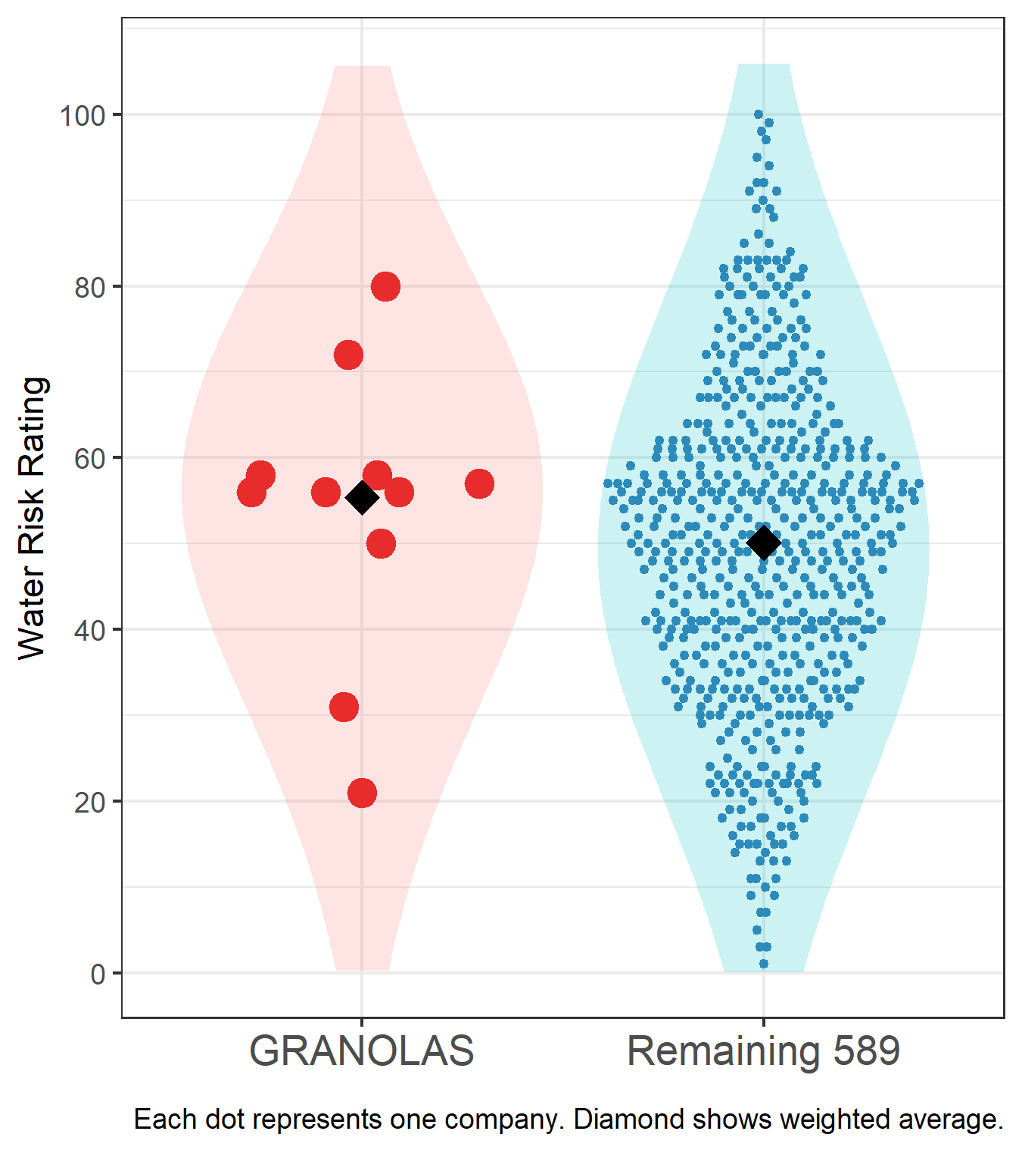
Regarding water risk, the industry diversification of the GRANOLAS paints a mixed picture. As shown, most of the GRANOLAS place above 50, indicating low risk. Nonetheless, two of the more consumer-oriented companies show high or medium risks, which have not been sufficiently addressed. On a weighted average basis, the GRANOLAS perform slightly better than the rest of the index at 55.4, while the remaining companies are at 50.1. The bottom performers on water risk may warrant further scrutiny, as water scarcity potentially disrupting operations or business models may represent an unanticipated risk.
Financial performance through an EVA lens
Looking beyond the ESG metrics, ISS ESG also calculates a Financial Rating that incorporates profitability and financial risk measures. The profitability aspect captures the level and trend of economic value creation based on EVA Margin (EVA/Sales) and EVA Spread (EVA/Capital). The risk portion incorporates stock price and profit volatility, as well as balance sheet and cash flow vulnerability, among other leverage measures.
Figure 7 illustrates the overall Financial Rating, which is assessed on a 1-4 scale, where higher values indicate better risk-adjusted profitability.
Figure 7: ISS ESG EVA Financial Rating (profitability and risk)
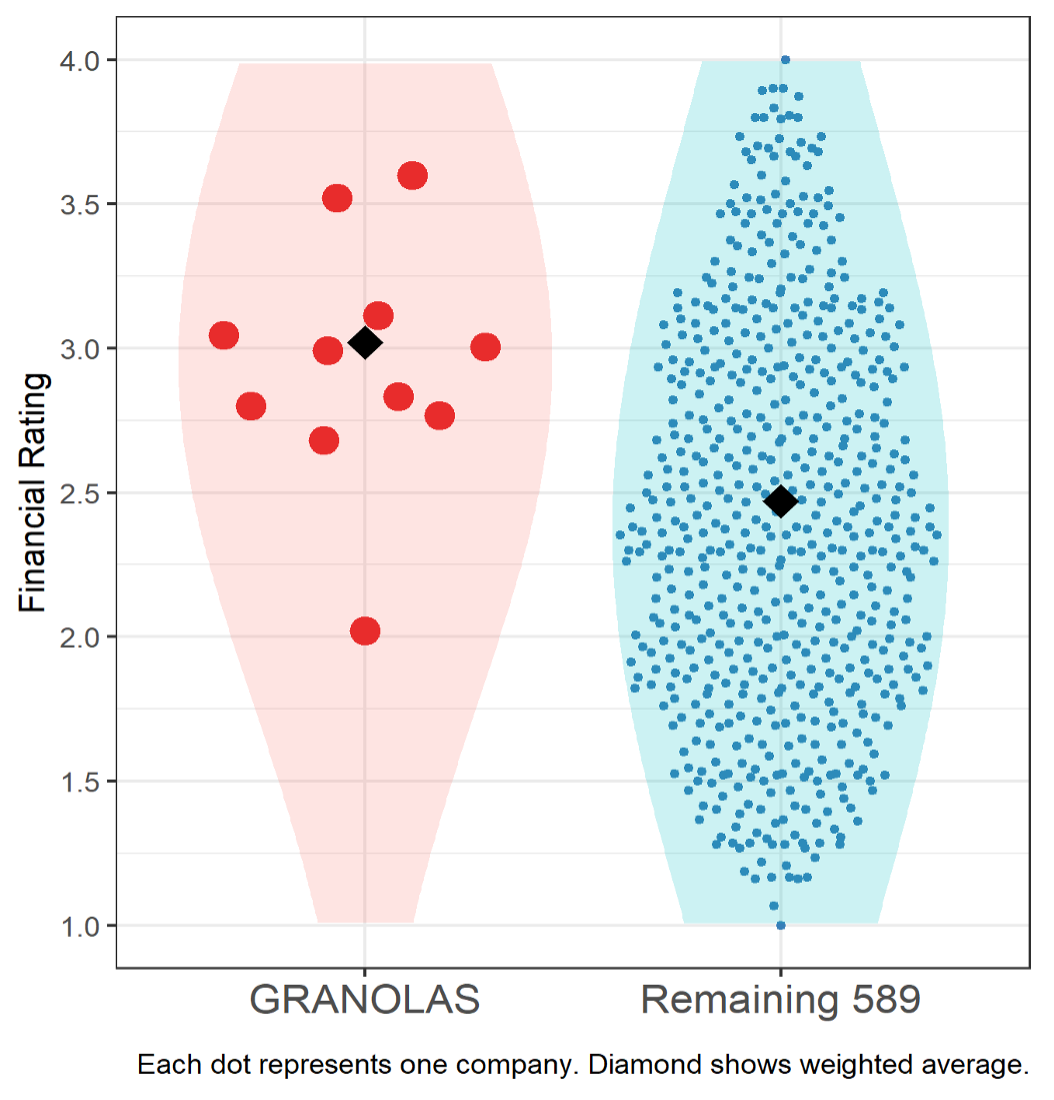
As shown, overall, the GRANOLAS’ weighted-average financial rating is comparatively strong and well above the remaining’ companies’ weighted average. On this basis, the GRANOLAS have a financial rating of 3.0, while the remaining companies are at 2.5. Nonetheless, we do note an outlier which performs comparatively weakly and below the average of the remaining companies. Given the GRANOLAS’ significant weight in the STOXX Europe 600 index, understanding where the financial vulnerabilities might lie could be of strong interest to investors.
A robust, holistic ESG picture with a sprinkling of potential vulnerabilities
In summary, as a companion to the recent sustainability review of the Magnificent 7, this article reviews identical ESG and climate metrics for the European GRANOLA stocks, comparing them with the remaining equities in the STOXX Europe 600 index. While many other metrics could be added to this analysis, these represent a broad cross-section of key sustainability issues.
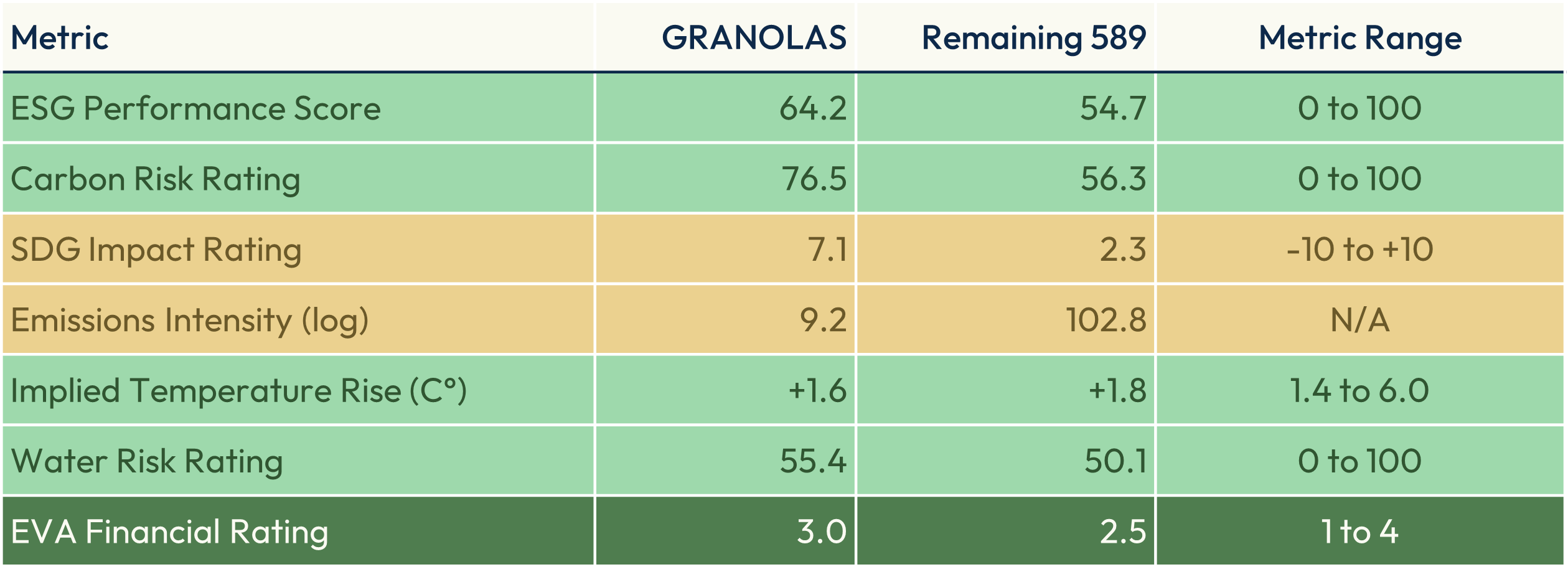
Overall, as shown in Figure 8, the GRANOLAS on average perform very robustly and ahead of the market average across overall ESG performance, carbon risk, SDGs, emissions and temperature scenario alignment, as well as water risk. They particularly stand out due to their high alignment with the U.N. SDGs, which is in large part due to the significant exposure to meeting healthcare needs.
Figure 8: GRANOLAS’ weighted-average sustainability and financial metrics
As a perhaps noteworthy summary for investors, Figure 9 leverages the previous research to show a direct comparison between the GRANOLAS and the Magnificent 7 across the metrics.
Figure 9: GRANOLAS’ and Magnificent 7’s weighted-average sustainability and financial metrics
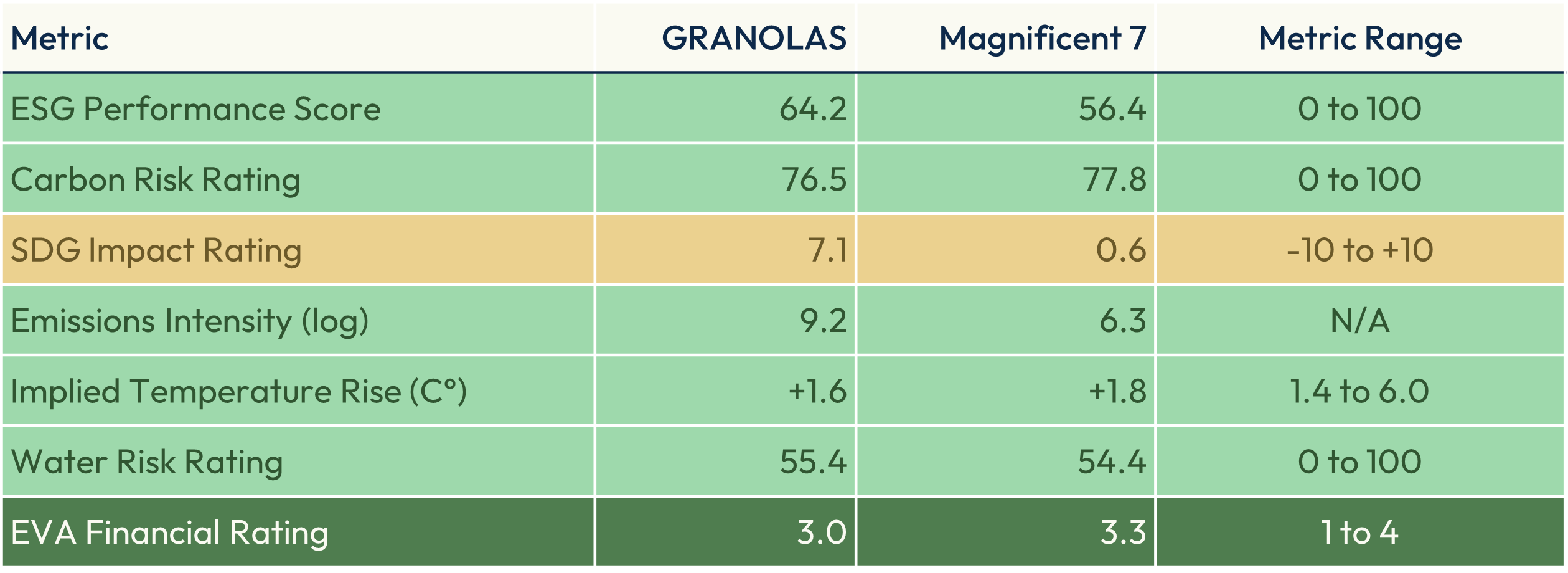
The GRANOLAS perform meaningfully better on ESG Score and Carbon Risk Rating. They perform similarly on emissions intensity, temperature rise and water risk. The most striking difference is on SDG alignment, where the GRANOLAS perform remarkably better than the Magnificent 7.
While the aggregate results in this article provide insight, for investors the most valuable aspect of this analysis might be to understand the dispersion within both groupings at the security level and the specific risks and opportunities individual corporate performance presents. Finally, the article also includes ISS ESG’s Economic Value Added-based financial rating, which also shows overall strength for the GRANOLAS, with a noteworthy outlier.
Explore ISS ESG solutions mentioned in this report:
- Identify ESG risks and seize investment opportunities with the ISS ESG Corporate Rating.
- Use ISS ESG Climate Solutions to help you gain a better understanding of your exposure to climate-related risks and use the insights to safeguard your investment portfolios.
- Understand the impacts of your investments and how they support the UN Sustainable Development Goals with the ISS ESG SDG Solutions Assessment and SDG Impact Rating.
- Develop engagement strategies, define achievable engagement objectives and manage your engagement process with ISS ESG’s Norm-Based Engagement Solution and Thematic Engagement Solution.
- Understand the F in ESGF using the ISS EVA solution.
